1,3-Butadiene (BD) is an important industrial chemical used as a building block precursor for synthetic rubber materials including tires, hoses, gaskets, and other polymer products. While BD serves critical industrial functions, questions have persisted about potential human health risks from environmental and occupational exposures, particularly regarding cancer and noncancer effects.
To evaluate current risk assessment methodologies, SciPinion conducted an independent review, recruiting experts specializing in toxicology, epidemiology, and quantitative risk assessment from a broad population of researchers. The expert panel was engaged using a modified Delphi format to provide input on key methodological decisions in the cancer and noncancer risk assessment for BD.
The expert panel validated current approaches for BD risk assessment. Their analysis confirmed that best available science approaches were appropriately applied, including incorporation of the most up-to-date datasets and prominent use of BD biomarkers for exposure assessment. The panel endorsed the use of Monte Carlo methods to incorporate information on uncertainty and variation in the risk assessment process.
Based on comprehensive evaluation of available science, data, and methodologies, the independent expert panel concluded that current and foreseeable BD exposures in the US population are not expected to pose an unreasonable risk of cancer or noncancer effects. The panel’s findings support the scientific rigor of existing regulatory frameworks for BD risk management and provide confidence in current public health protection measures.
- View the published manuscript.
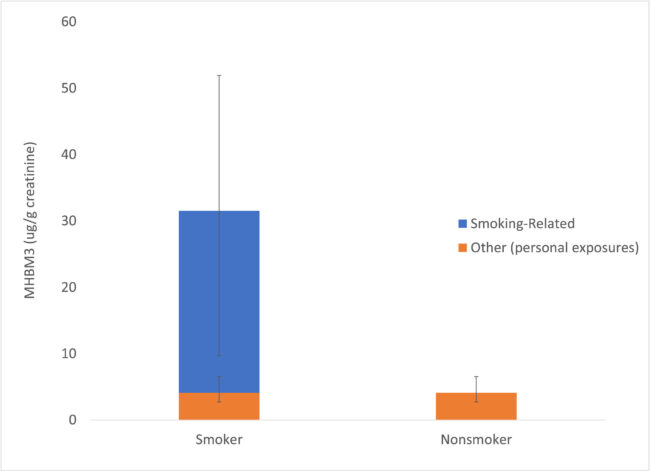
Figure 1. BD Urinary Biomarker (4HEBMA) in Smokers and Nonsmokers (Nieto et al., 2021); The column heights indicate the median values, error bars indicate the 25th and 75th percentile values.